Polymeric Drop-Out Fuse
When the current operating through an electrical circuit exceeds a certain limit, a drop-out fuse trips the circuit. This threshold is set by the fuse’s current rating, typically expressed in amperes. The fuse element melts in the case of over-current or a short circuit, cutting off the circuit and preventing further damage to the electrical system. These fuses are sensitive to temperature variations and over-current conditions.
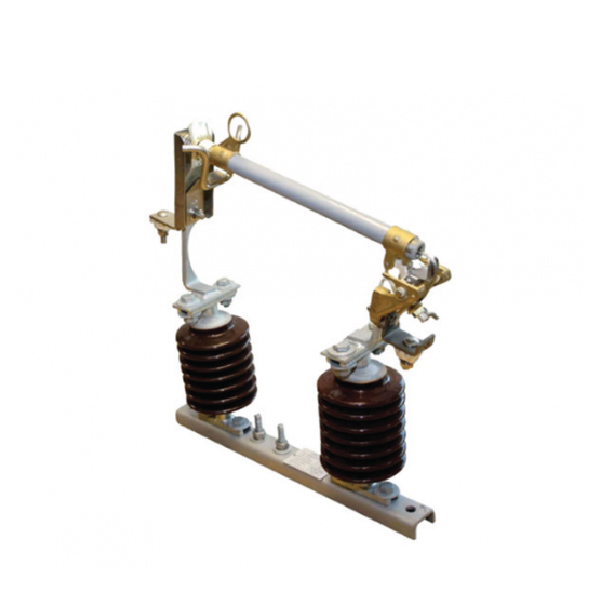
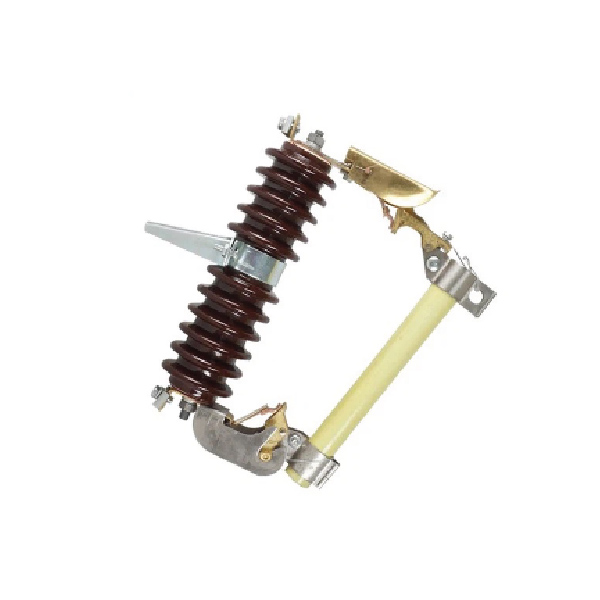
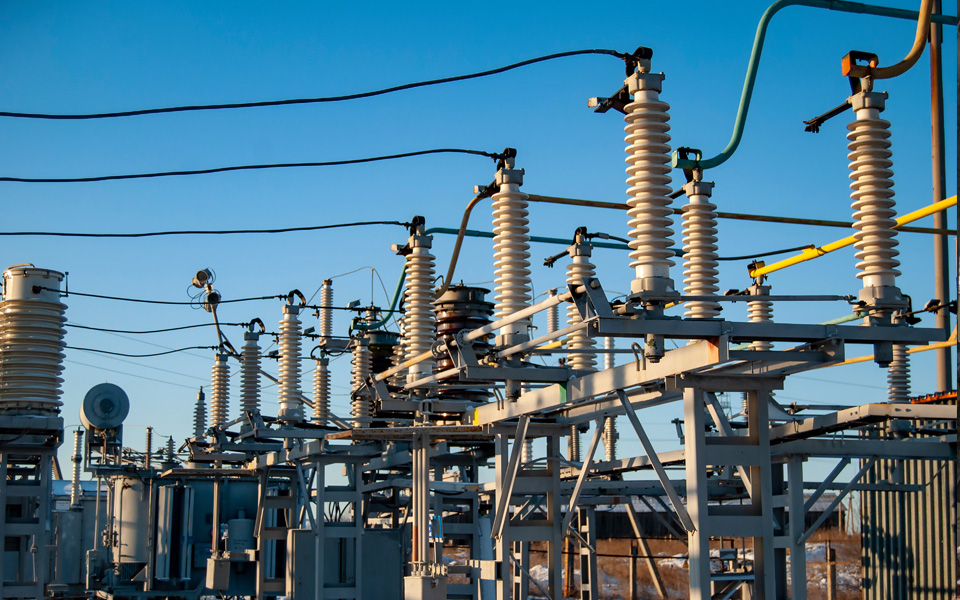
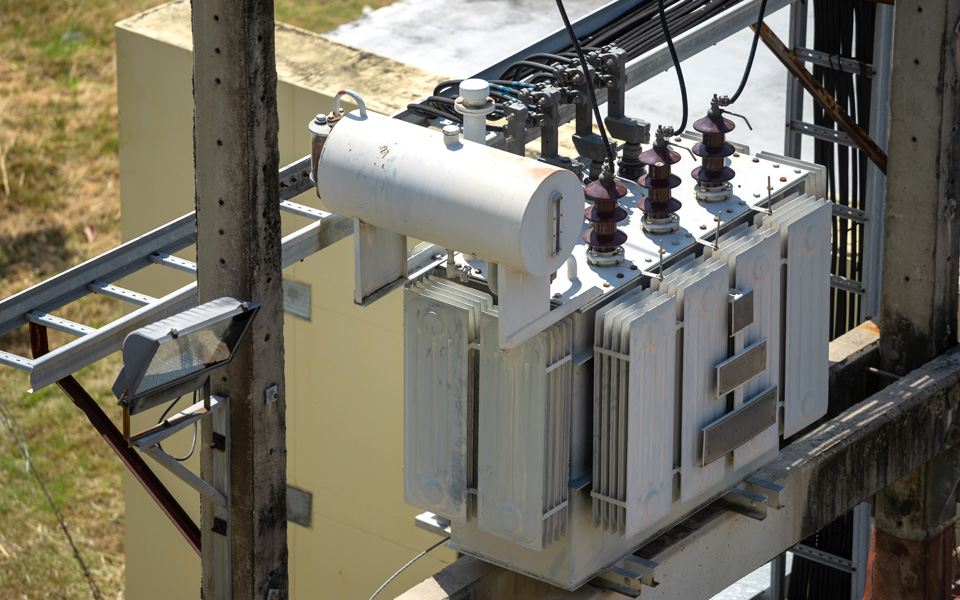
A Polymeric Drop-Out Fuse is an advanced protective device used in electrical distribution systems to provide overcurrent protection and enhance operational reliability. It is characterized by its use of high-performance polymeric materials, which offer superior insulation and durability compared to traditional materials.
How It Works
The Polymeric Drop-Out Fuse contains a fusible element housed within a robust polymeric insulator. When a fault current occurs, the fusible element melts, causing an arc that is quickly extinguished by the insulating properties of the polymeric material. The drop-out mechanism then activates, allowing the fuse holder to fall away, visibly disconnecting the circuit and signaling the need for fuse replacement.
Applications:
Polymeric Drop-Out Fuses are widely utilized in:
The use of polymeric materials offers enhanced weather resistance, longevity, and safety, making Polymeric Drop-Out Fuses a preferred choice for modern electrical distribution systems requiring high reliability and low maintenance.
Made of polymer materials such as epoxy or silicone rubber, they are robust against external influences and lightweight.
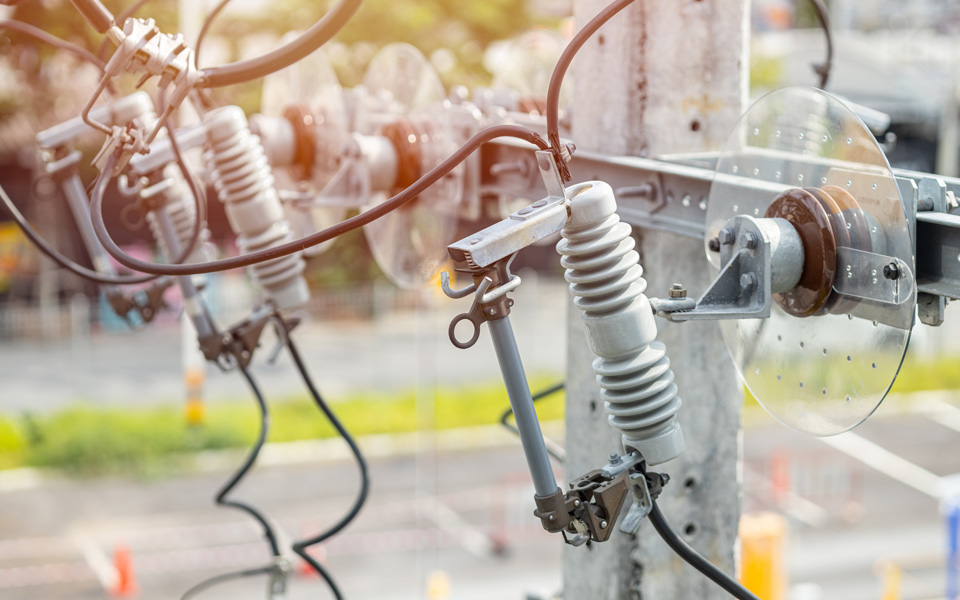
Commonly used in urban areas, compact substations, distribution networks, and substations where transformers and distribution lines utilize it.
Overhead Power Distribution

Renewable Energy Systems

Industrial & Commercial Electrical Systems