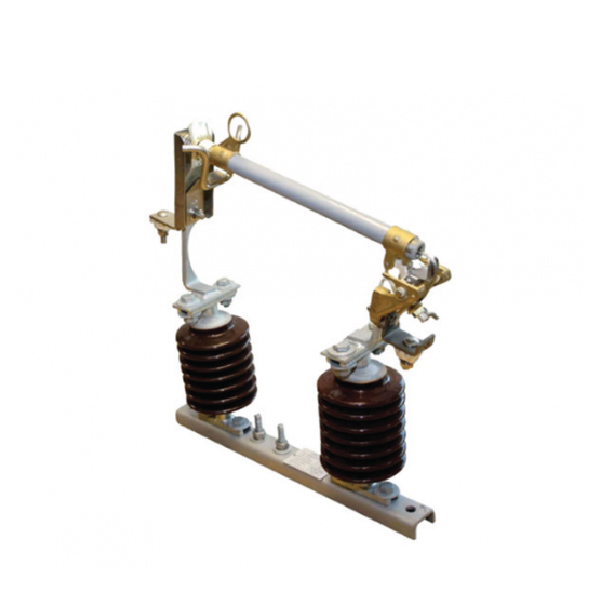
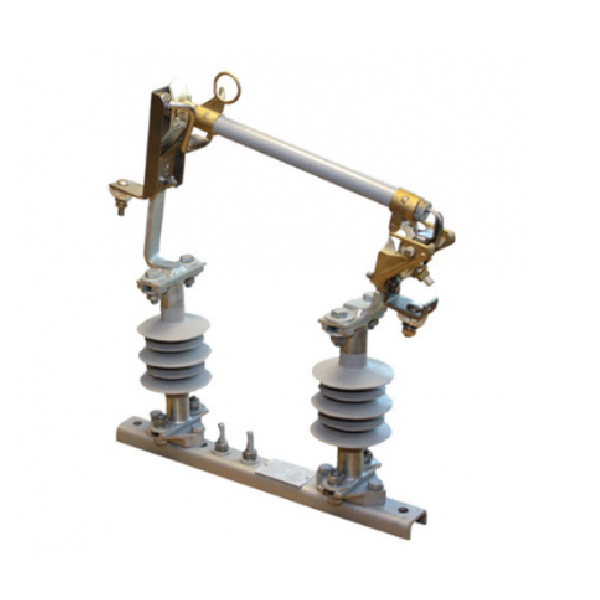
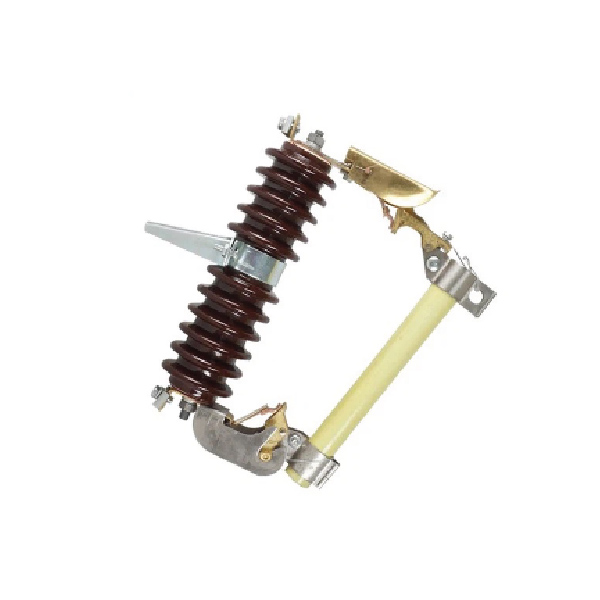
Expulsion Drop-Out Fuse
When the current operating through an electrical circuit exceeds a certain limit, a drop-out fuse trips the circuit. This threshold is set by the fuse’s current rating, typically expressed in amperes. The fuse element melts in the case of over-current or a short circuit, cutting off the circuit and preventing further damage to the electrical system. These fuses are sensitive to temperature variations and over-current conditions.
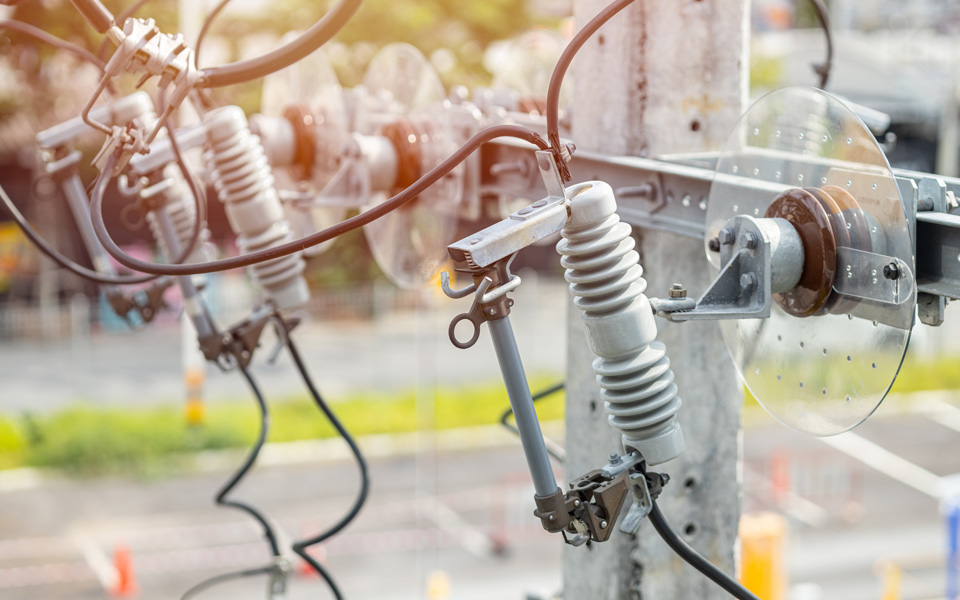
An Expulsion Drop-out Fuse is a protective device used in electrical systems to safeguard equipment and maintain system stability. It combines the features of an expulsion fuse and a drop-out mechanism to offer reliable overcurrent protection and visual indication of a fault.
How It Works
The fuse consists of a fusible element housed within an insulating tube filled with arc-quenching materials. When a fault current occurs, the fusible element melts, creating an arc that is extinguished by the insulating material. The drop-out mechanism then releases the fuse carrier, causing it to fall open under gravity, which visibly disconnects the circuit and signals the need for maintenance.
Applications:
Expulsion Drop-out Fuses are commonly used in:
Their ability to provide both protection and a clear visual indicator of faults makes Expulsion Drop-out fuses an essential component in various electrical distribution systems.
Consists of high-purity quartz sand inside a porcelain tube and copper or tin fuse element is located inside the tube.
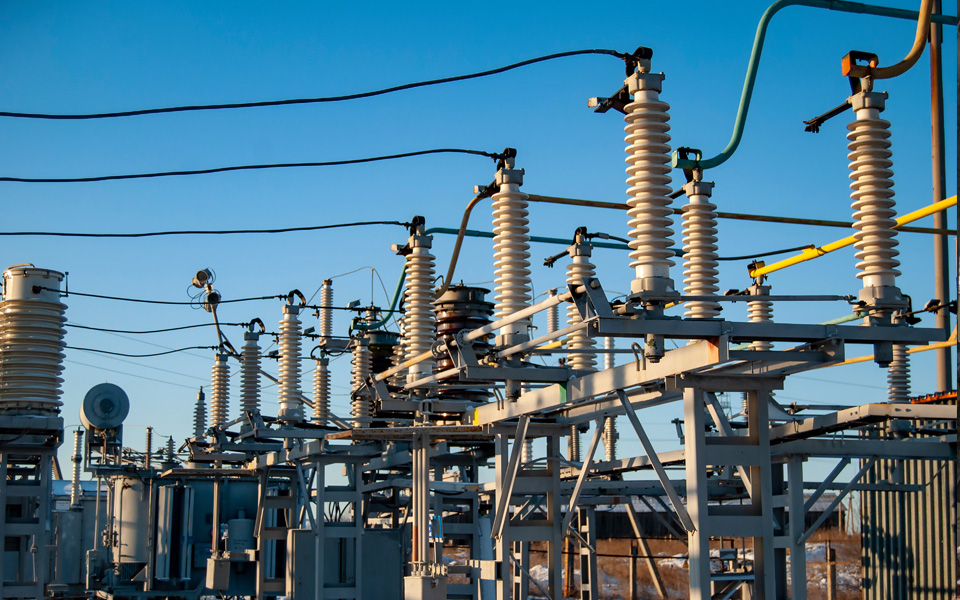
Overhead Distribution Lines

Rural Electrification

Industrial Plants